Before migrating to Redis Cloud, you should evaluate the migration and consider the best option. Read this guide to determine which migration strategy is right for you.
[email protected]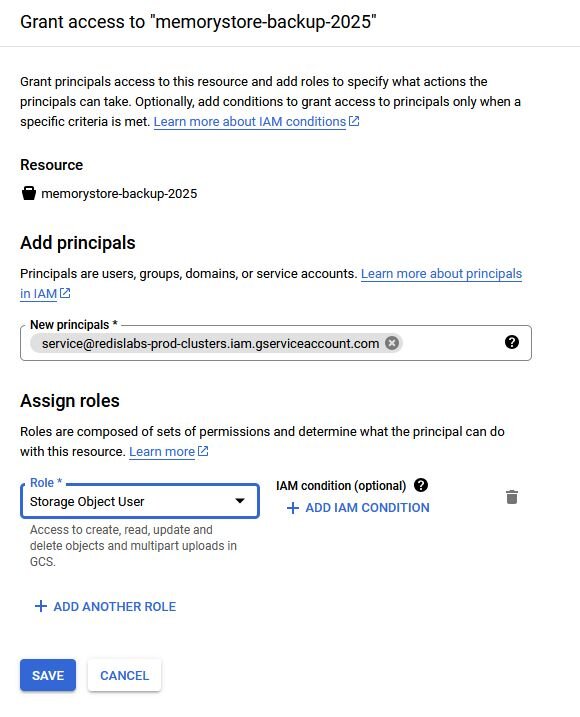
gs://bucketname/[path/]filename.rdb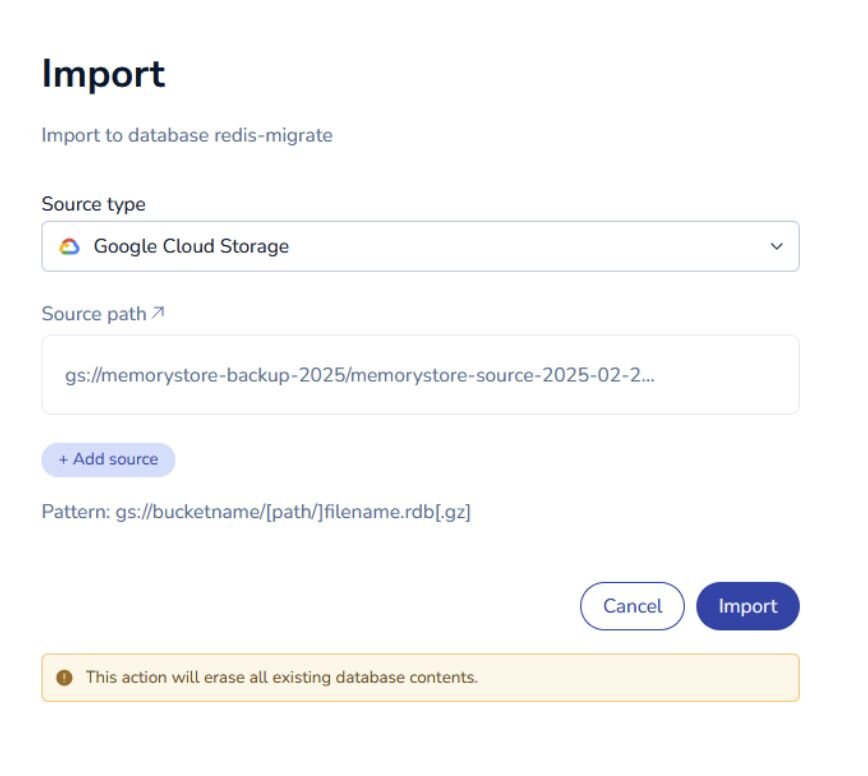
Your Memorystore instance must be accessed from a Compute Engine instance with proper permissions. The following guide assumes that your Memorystore instance is reachable from the internet via a Compute Engine instance.
3. Verify the connectivity with the Memorystore instance, replace MEMORYSTORE_ENDPOINT with your Memorystore endpoint.
4. Install Java, we recommended using OpenJDK 21 or later:
5. Install RIOT. Download the desired release. Then, unzip the package and make sure the RIOT binaries are in place, as shown here:
6. You can check the version of RIOT by running the command below:
Once Java and RIOT are installed, you are all set to begin the migration process which replicates data directly from the source (Memory) to the target (Redis Cloud).
sudo ./riot replicate redis://MEMORYSTORE_ENDPOINT:port redis://username:password@REDIS_CLOUD_ENDPOINT:port --mode liveNote:
The live replication mechanism does not guarantee data consistency. Redis sends keyspace notifications over pub/sub which does not provide guaranteed delivery. It is possible that RIOT can miss some notifications in case of network failures for example.
Also, depending on the type, size, and rate of change of data structures on the source it is possible that RIOT cannot keep up with the change stream. For example if a big set is repeatedly updated, RIOT will need to read the whole set on each update and transfer it over to the target database. With a big-enough set, RIOT could fall behind and the internal queue could fill up leading up to updates being dropped.
For those potentially problematic migrations it is recommended to perform some preliminary sizing using Redis statistics and bigkeys/memkeys in tandem with --mem-limit. If you need assistance please contact your Redis account team.
For more information, see:
sudo apt update && sudo apt install -y redis-toolsredis-cli -h MEMORYSTORE_ENDPOINT -p 6379sudo apt install -y openjdk-21-jdkwget https://github.com/redis/riot/releases/download/v4.2.3/riot-4.2.3.tar && tar -xvf riot-4.2.3.tar && cd riot-4.2.3/bin/./riot --version------------------------------------------------------------
riot 4.2.3
------------------------------------------------------------
Build time: 2025-02-16 18:35:57Z
Revision: d7a319522e4e72a2b5277e5a15bd715d557dedb6
JVM: 21.0.6 (Ubuntu 21.0.6+7-Ubuntu-120.04.1)
------------------------------------------------------------